Government of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa
Government of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa
Government of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa
Government of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa
- Celebrating Independence Day & Honoring Pakistan’s Triumph
- CEO KPT&GSC Conducts Progress Review of 132/220kV Gorkin-Matiltan Transmission Line Project
- Job Opportunity for the Post of CEO KPT&GSC
- 10th Board meeting of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Transmission & Grid System Company (KPT&GSC)
- KP Transmission and Grid System Company Review Meeting Yields Strategic Expansion Plans
Welcome to KPT&GSC
KP Transmission & Grid System Company is state of art company established by the Govt of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, NEPRA issued license on 26.02.2021. Registered with SECP on 04.09.2020 as Multi-Member Company (MMC). KP Transmission & Grid System Company can lay down all kind of transmission & distribution network within the province.

Engr. Luqman Hakeem Khan
CEO KPT&GSC
ceo@kptgc.gov.pk

Muhammad Zubair
Secretary E&P Deptt

KPT&GSC
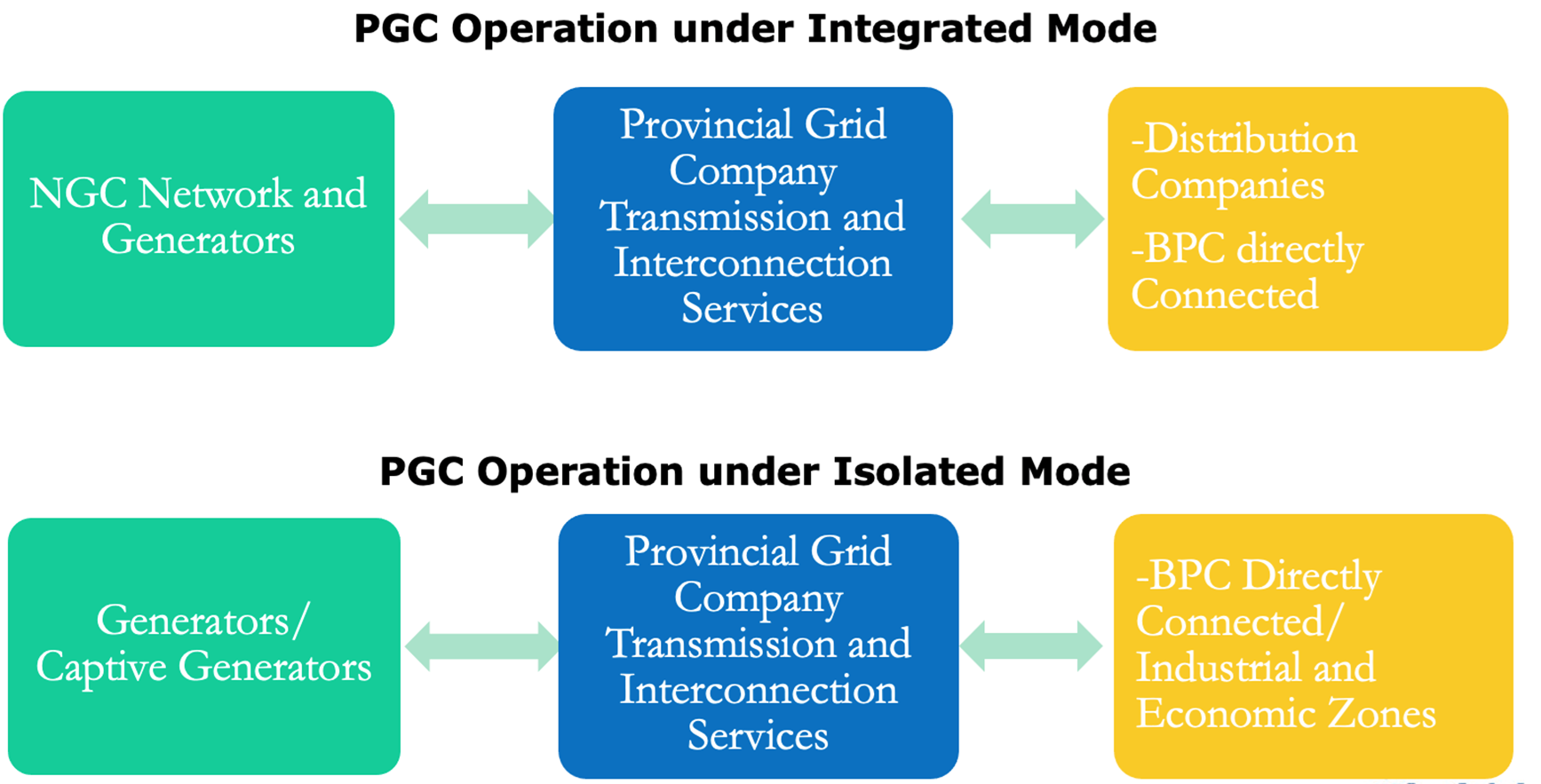
NEED FOR PROVINCIAL GRID COMPANY
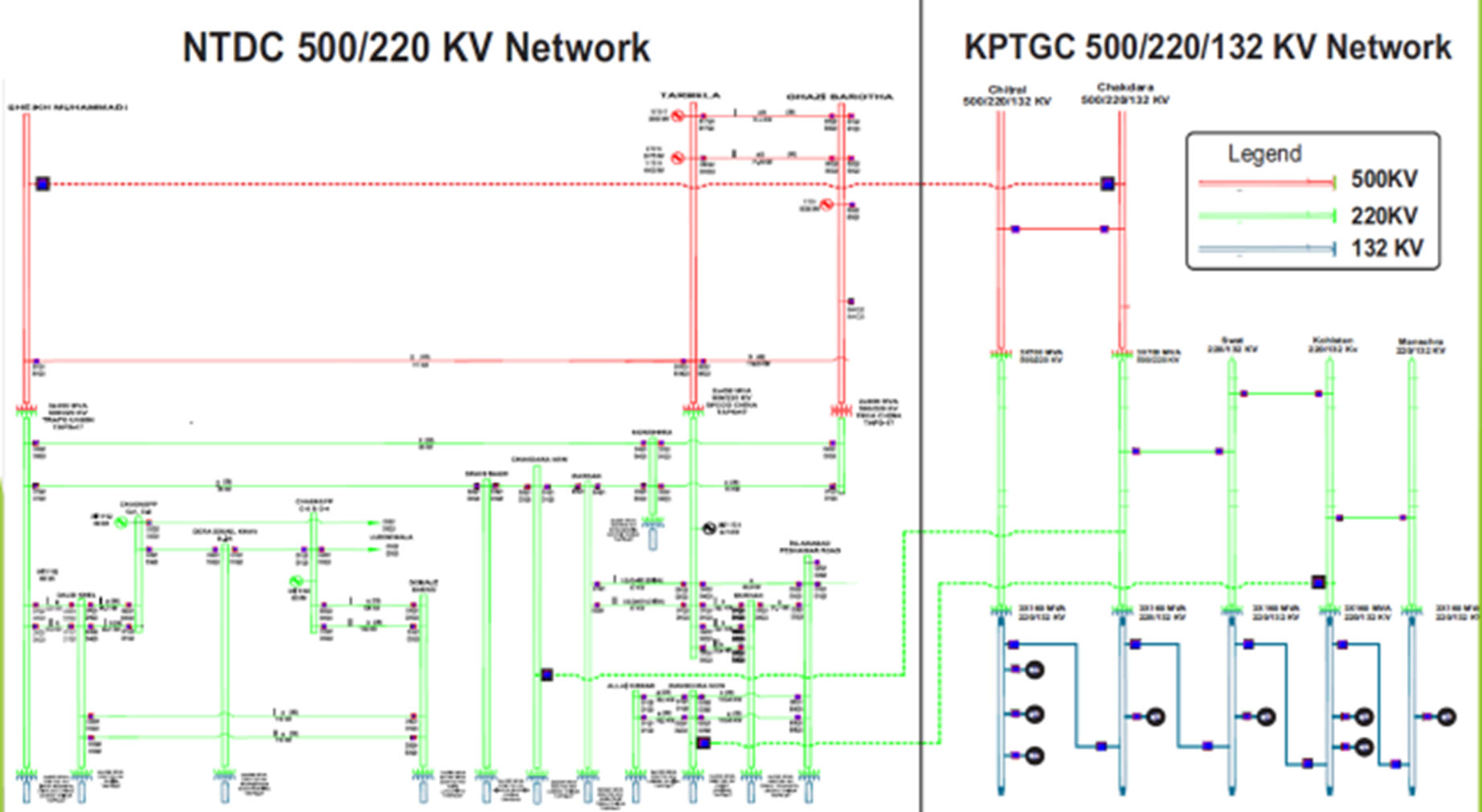
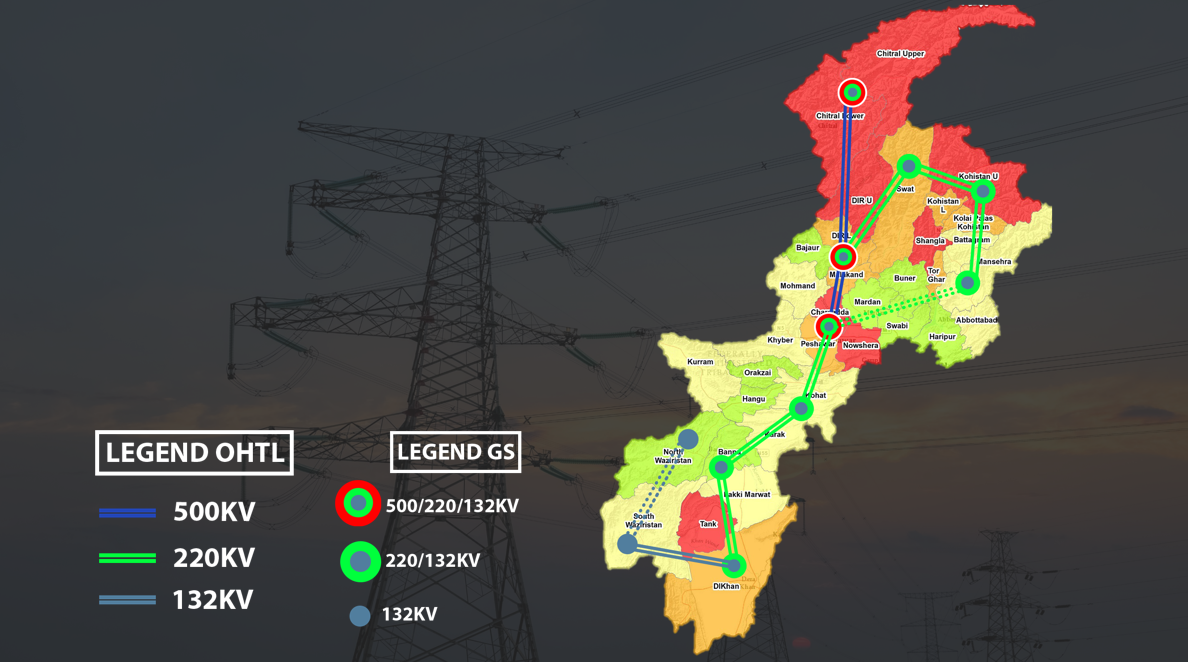
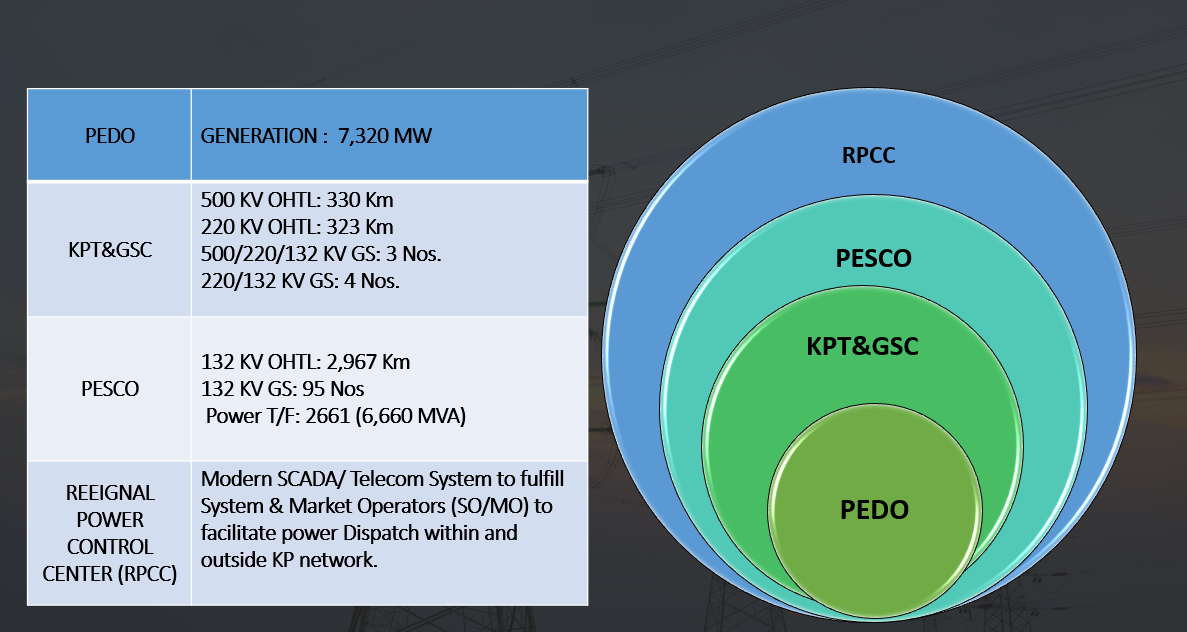
KPT&GSC NETWORKS
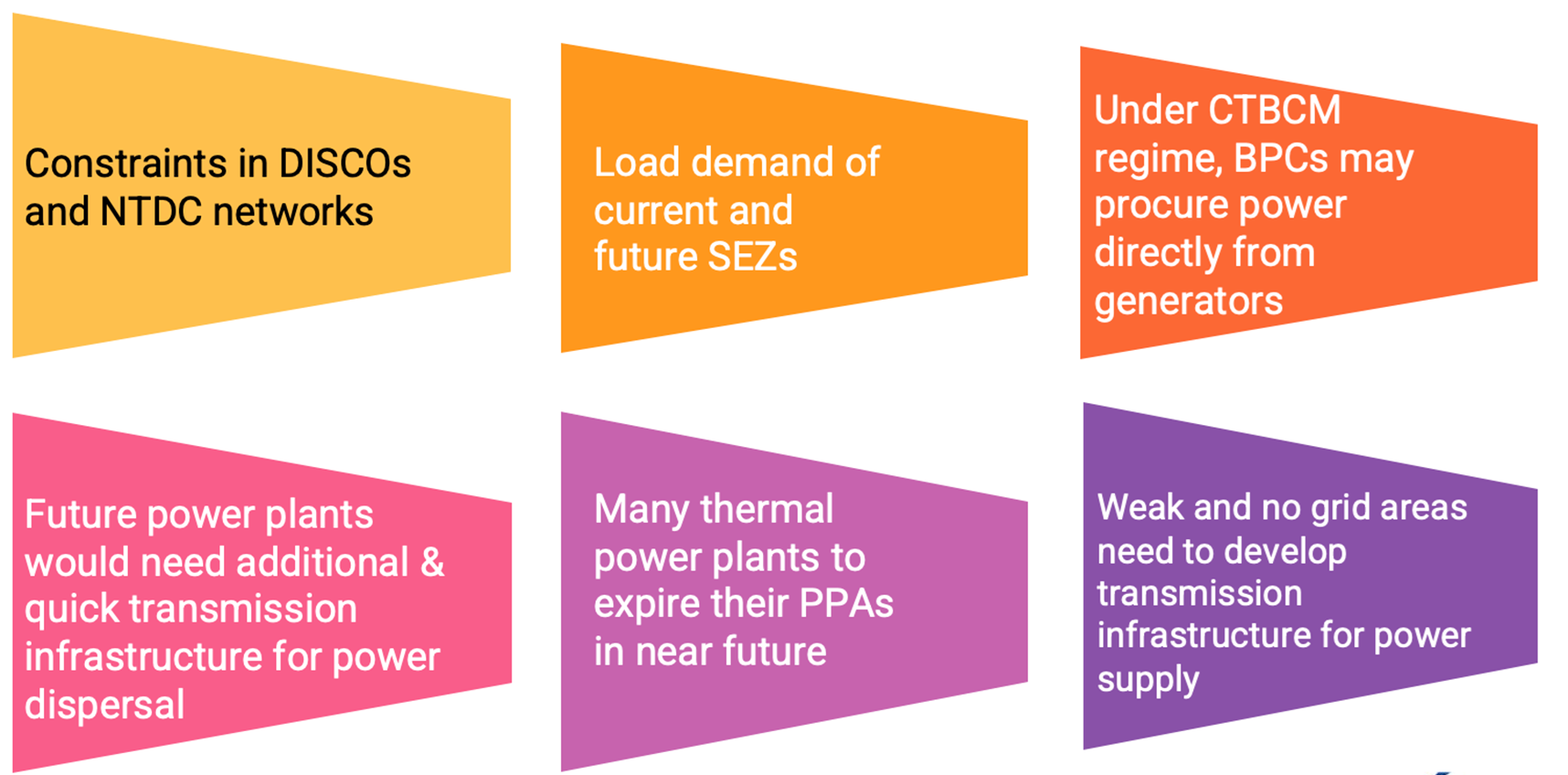
OPPORTUNITIES & CHALLENGES
The transition to CTMCB has created many challenges and opportunities for the entities/stack holders being involved in Generation, Transmission, Distribution and utilization of electric power. Under the emerging scenario, PEDO and KPT&GSC has to review and position itself of the challenges ahead of the emerging market in a bid to exploit its strengths, and to counter the weakness in order to take maximum benefits of the power wholesale market.
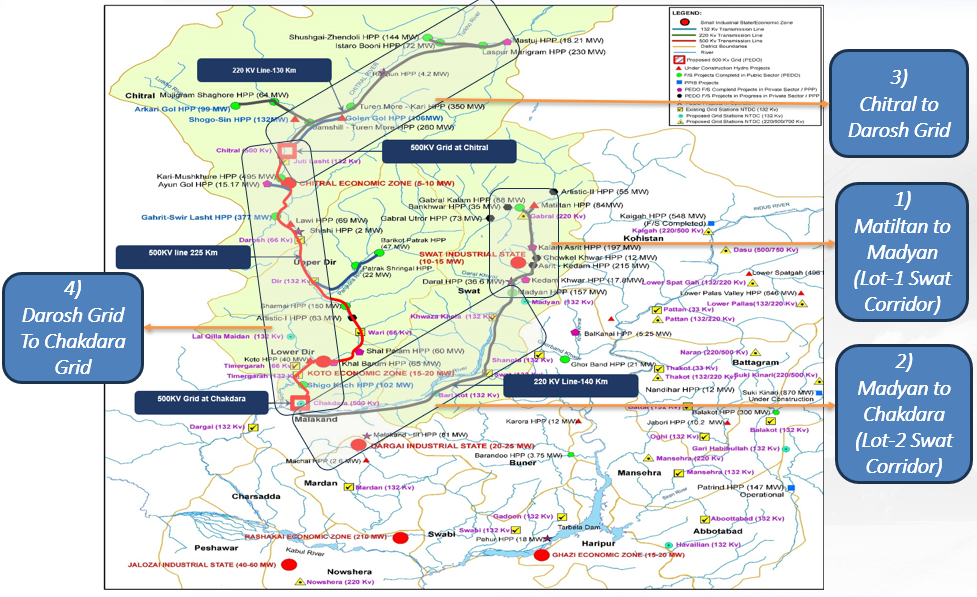
The KP Province is in dire needs for proactive measures to protect its interest, mitigate the effects of open access and turn it into its favor for PEDO HPP powers evacuation to load centers through fast track OHTL Projects, which comprise the following. The below four (4) major scenario arises.
Supply of electricity through KPT& GSC constructed Network ( To evacuate Power from Upcoming PEDO HPPs)
Supply of electricity through Construction of new O/H Transmission lines to cover PEDO running HPPs and offset the affects of open access regime.
Supply of electricity through Direct Supply Model: To establish industrial plants adjacent/close vicinity to PEDO hydel power plants and benefit from the lower cost of hydel electricity:
As last Resort, to supply of electricity through other stack holders networks under CTBCM open access regime.
KP ECONOMIC REVIVAL THROUGH ENERGY MIX OF HYDROPOWER, SOLAR CAPTIVE POWER & THERMAL POWER FROM LOCAL GAS.
- To mitigate KP location disadvantages and to convert a liability into an asset, and to attract investors and industry from other provinces and abroad, the KP economic survival is based in the availability of a cheap energy mix to be tapped off from hydro, Solar , Local gas and Municipal Solid Waste (MSW).
- The expensive generation cost per KWh are RLNG (Rs.51.42), Furnace oil (Rs.48.36), imported coal (Rs.33.64) , followed by the medium range generation cost: Wind power (Rs 33.64), local coal (Rs 23.97) and Nuclear (Rs.18.38) .The cheapest generation cost are: Hydro (Rs.6.94), Local Gas (Rs.13.02) and Solar (Rs. 15.04)
- The Economic Zones developed under KP Economic Zones Development and Management Company (KPEZDMC) have indicated below loads for EZ & SEZ . ( The EZ & SEZ loads with more than 20 MW are listed below )
1. Existing economic zones 2. Newly Established Economic Zones
- Hattar Economic Zone: 136 MW Rashakai Economic Zone: 210 MW
- Gadoon Economic Zone; 85 MW Hattar Special Economic Zone: 160 MW
- Peshawar Economic Zone: 80 MW Dara band Economic Zone : 370 MW
- Mohmand Economic Zone: 40 MW
- Hydro: The KPT&GSC is planning to construct a 132 kV transmission lines or of lower KV level to link PEDO running HPPs power (148 MW) with KP & SEZ industrial sectors. The Malakand III HPP (81 MW) will be linked to Rashakai Economic Zone ( 210 MW ) . The project looks feasible with a cost of Rs. PKR /benefit ratio. Presently, power from economic Malakand III HPP is fed to national grid. The project cost is around PKR 2.5 Billion with a revenue forecast of PKR 6.8 Billion/annum.
- Solar : The office of SEC (E &P) under SIFC umbrella is negotiating a 1000 MW renewable project with a JV of Canadian Commercial Corporation (CCC) – the investor and DAI Inc. Canada- the constructor, through the courtesy of HBS Group, Islamabad –the facilitator: The realization of this project will not only resolve KP EZ and SEZ energy supply issues (through solar) , but provide a leap forward for KP province to enter into an energy mix arena and energy sustainability through provision of a stable, reliable and affordable power
- Local Gas: Addition of Thermal Generation from local gas – KP South. A feasibility study has already been conducted through the support of US Trade and Development Authority for CCGC thermal plants, Kohat – 435 MW ( Phase -1) and 435 MW x 2 ( Phase -2) . The estimated cost of the project is US $ 567 Million (Phase-1) and shall be executed under a PPP mode . The project apart from to deliver enormous socio-economic benefits to the KP province, will pave way for development of indigenous gas power sector. The Project needs a revival under a firm political commitment for commencement, execution and completion.
- Generation from Municipal Solid Waste Management (MSM). PDA & Water & Sanitation Services, Peshawar (WSSP) has conducted feasibility for a 20 MW (148.92 GWh energy) MSW Energy Plant , Peshawar based on 1000 Tons waste availability /day . The levelized tariff for MSM energy productions cost is around US 10-12 cent/KWh, and further, is dependent upon the quantum of wastage available/day. A project of similar nature is under consideration by Mardan Development Authority (MDA) for a 12 MW WSM plant.
- The Punjab government is working on a 35 MW waste management plant, Lahore with a 2000 ton wastage available/day.
- WtE is a sustainable process with lot of benefits such as:
I. A stable and reliable power supply for Peshawar .
II. Support to mitigates issues relating to air, water and land pollutions.
III. Reduction of environmental and social problems at the disposal site.
IV. Reduction/elimination of land fills toxins.
V. Reduction in GHG emission reduction
VI. Protection of ground water contamination leading to cancer, hepatitis and respiratory problems, and which also affects plants and habitat.